Title: The Importance of the Spine: Functions and Benefits
Introduction
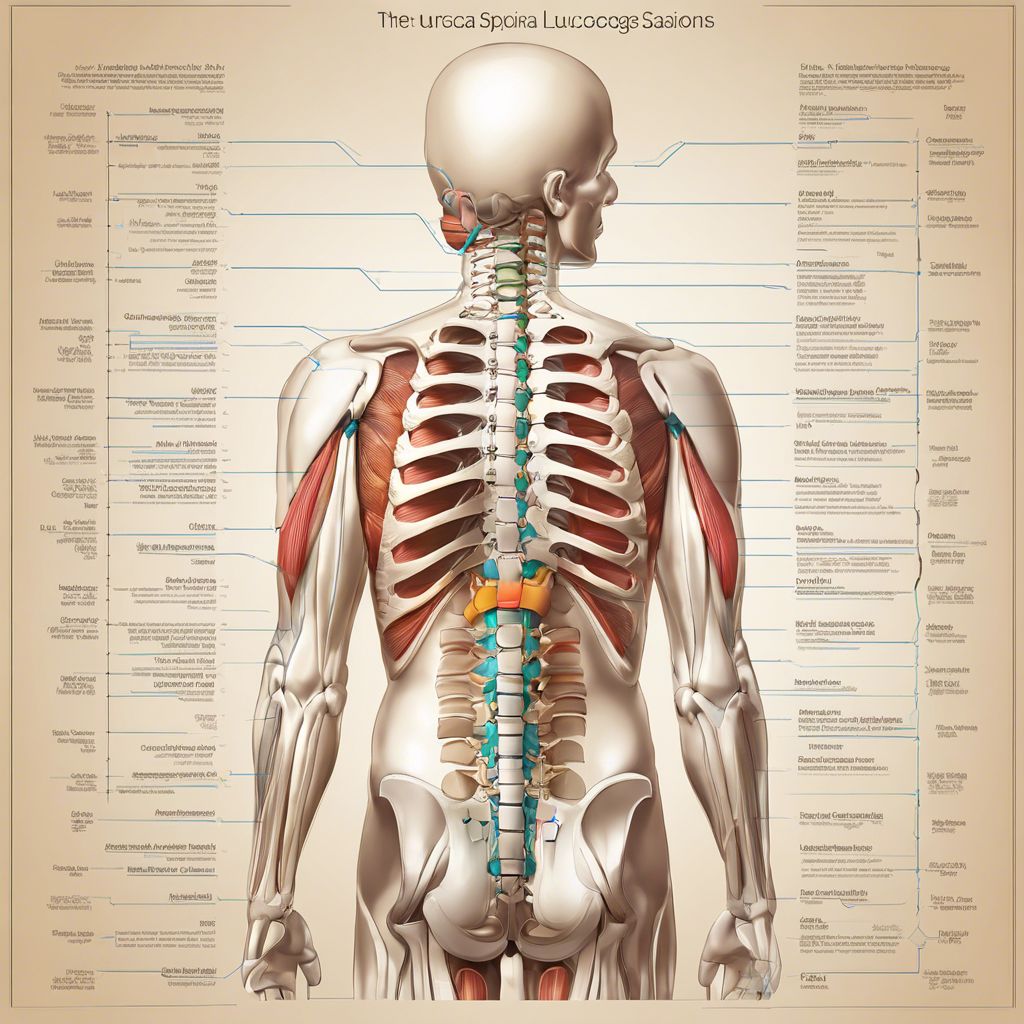
The spine, also known as the vertebral column, is a crucial part of the human skeleton. It plays a vital role in overall body function and health. Composed of 33 vertebrae, the spine supports the body, protects the spinal cord, and enables movement. This article will explore the various benefits of the spine and its essential functions.
1. Structure of the Spine
The spine is divided into five regions, each with a specific number of vertebrae:
a. Cervical Region
The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae (C1-C7) located in the neck. It supports the head and allows for a range of movements, including rotation and flexion.
b. Thoracic Region
The thoracic spine consists of twelve vertebrae (T1-T12) and is connected to the ribs. It provides stability and protects the organs in the chest cavity.
c. Lumbar Region
The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae (L1-L5) in the lower back. This region bears the majority of the body’s weight and allows for flexibility and movement.
d. Sacral Region
The sacral spine is made up of five fused vertebrae (S1-S5) that form the back of the pelvis. It supports the weight of the upper body when sitting and standing.
e. Coccygeal Region
The coccygeal spine consists of four fused vertebrae that form the tailbone. It serves as an attachment point for ligaments and muscles.
2. Functions of the Spine
a. Support and Stability
The spine provides structural support for the body, allowing us to stand upright and maintain proper posture. It helps distribute weight evenly across the body, reducing the risk of injury.
b. Protection of the Spinal Cord
The spinal cord, which runs through the vertebral column, is a critical part of the central nervous system. The spine protects the spinal cord from injury, ensuring that signals between the brain and the body can be transmitted effectively.
c. Flexibility and Movement
The spine allows for a wide range of motion, enabling activities such as bending, twisting, and lifting. The intervertebral discs between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers, permitting flexibility while maintaining stability.
d. Absorption of Shock
The spine absorbs shock during movement, helping to protect the brain and spinal cord from impact. This function is particularly important during activities such as running or jumping.
e. Role in Posture
A healthy spine is essential for maintaining good posture. Proper alignment of the spine reduces strain on muscles and ligaments, preventing discomfort and long-term damage.
3. Importance of Spine Health
Maintaining a healthy spine is crucial for overall well-being. Poor posture, lack of exercise, and injuries can lead to spinal problems such as herniated discs, scoliosis, and chronic pain. To promote spine health, consider the following tips:
a. Exercise Regularly
Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the muscles that support the spine, promoting better posture and flexibility.
b. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight can strain the spine, leading to discomfort and potential injury. Maintaining a healthy weight supports spinal health.
c. Practice Good Posture
Being mindful of posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can prevent strain on the spine and reduce the risk of injury.
d. Seek Professional Help
If experiencing persistent back pain or discomfort, consult a healthcare professional for assessment and treatment.
Conclusion
The spine is a vital component of the human body, providing support, protection, flexibility, and stability. Understanding its functions and benefits can help individuals prioritize spine health and take proactive steps to maintain it. A healthy spine contributes significantly to overall well-being and quality of life.
Sources
1. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
2. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
3. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques
4. Spine Health